NASA seeks to break the “tyranny of launch” with in-space manufacturing
Ars Technica » Scientific Method 2019-07-29
-
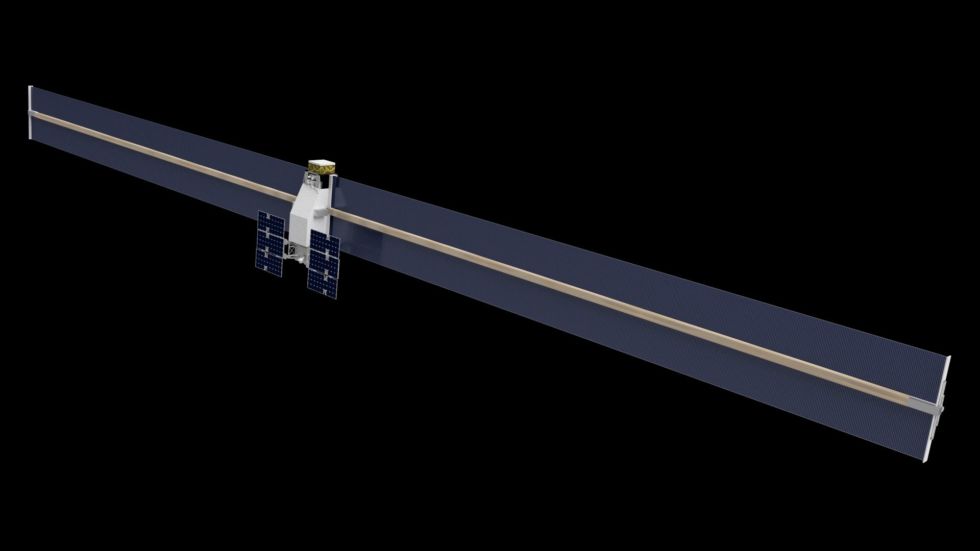
The Archinaut One satellite, illustrated above, will use robotic manufacturing and assembly to manufacture two 10-meter solar arrays in orbit. [credit: Made in Space ]
Made in Space is one of the most intriguing companies in aerospace because it's not so much focused on getting into space. Rather, the company is focused on doing interesting, meaningful, and potentially profitable things once there. Its long-term goal is to build factories in space using additive manufacturing.
A recent NASA contract, worth $73.7 million, will allow Made in Space to significantly accelerate those efforts. "For us, this is one of those watershed moments that take this technology and propel it into the next stage," said Andrew Rush, president and chief executive officer, in an interview with Ars. Made in Space started the year with 40 employees and will end it with nearly 100.
The NASA contract will fund the company to build and fly a spacecraft it calls Archinaut One, with the aim of constructing two 10-meter solar arrays in orbit. These two arrays will power an ESPA-class satellite. (These are fairly small satellites, about 200kg, that are typically carried as secondary payloads by large rockets such as the Falcon 9 booster built by SpaceX.)