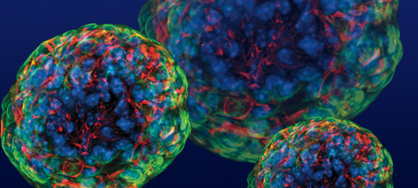
Acid bath turns cells from any tissue into stem cells
Ars Technica » Scientific Method 2014-01-30
The development of human embryonic stem cells, which have the ability to form any cell in the body, may enable us to repair tissues damaged by injury or disease. Initially, these cells could only be obtained through methods that some deemed ethically unacceptable, but researchers eventually developed a combination of genes that could reprogram most cells into an embryonic-like state. That worked great for studies, but wasn't going to work for medical uses, since one of the genes involved has been associated with cancer.
Researchers have since been focusing on whittling down the requirements needed for getting a cell to behave like a stem cell. Now, researchers have figured out a radically simplified process: expose the cells to acidic conditions, then put them in conditions that stem cells grow well in. After a week, it's possible to direct these cells into a state that's even more flexible than embryonic stem cells.
The catalyst for this work is rather unusual. The researchers were motivated by something that works in plants: expose individual plant cells to acidic conditions, grow them in hormones that normally direct plant development, and you can get a whole plant back out. But we're talking about plants here, which evolved with multicellularity and with specialized tissues in a lineage that's completely separate from that of animals. So there's absolutely no reason to suspect that animal cells would react in a similar way to acid treatment—and a number of reasons to expect they wouldn't.
Read 7 remaining paragraphs | Comments