Gravitational lens magnifies earliest galaxy yet seen
Ars Technica » Scientific Method 2012-11-19
The Universe's first galaxies played a key role in shaping the environment in which we now find ourselves. They fostered the formation of the first stars, which died in spectacular explosions that enabled a new generation of smaller stars, orbited by rockier planets. And the galaxies themselves merged and grew, forming the large galaxies and clusters that populate the Universe today. But, despite their critical role in shaping the Universe, we've never actually been able to see one of them.
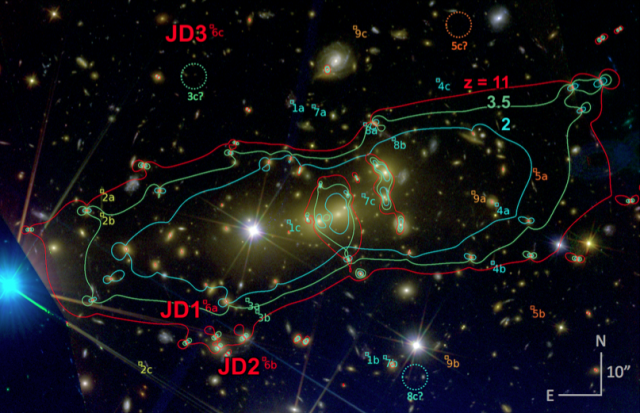
Slowly, that's changing. The Hubble Deep Field exposures have helped us spot galaxies from the Universe's early days. But now, a special Hubble project has used an intervening cluster of galaxies as a lens to spot what appears to be the most distant galaxy ever imaged, one that dates from just 425 million years after the Big Bang.
Since it takes light time to reach us from distant corners of the Universe, the further you look, the older the objects you see. The wavelength of the light also gets shifted towards the red by the expansion of the Universe, which stretches it out as it travels. As you get closer to the Big Bang, light that started out in the UV end of the spectrum gets pushed deeper and deeper into the infrared. To make these galaxies even harder to spot, the extreme distance means that very few photons actually make their way to Earth, so these objects are incredibly dim.
Read 6 remaining paragraphs | Comments