Whistleblower: Ubiquiti Breach “Catastrophic”
Krebs on Security 2021-03-31
On Jan. 11, Ubiquiti Inc. [NYSE:UI] — a major vendor of cloud-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as routers, network video recorders and security cameras — disclosed that a breach involving a third-party cloud provider had exposed customer account credentials. Now a source who participated in the response to that breach alleges Ubiquiti massively downplayed a “catastrophic” incident to minimize the hit to its stock price, and that the third-party cloud provider claim was a fabrication.

A security professional at Ubiquiti who helped the company respond to the two-month breach beginning in December 2020 contacted KrebsOnSecurity after raising his concerns with both Ubiquiti’s whistleblower hotline and with European data protection authorities. The source — we’ll call him Adam — spoke on condition of anonymity for fear of retribution by Ubiquiti.
“It was catastrophically worse than reported, and legal silenced and overruled efforts to decisively protect customers,” Adam wrote in a letter to the European Data Protection Supervisor. “The breach was massive, customer data was at risk, access to customers’ devices deployed in corporations and homes around the world was at risk.”
Ubiquiti has not responded to repeated requests for comment.
According to Adam, the hackers obtained full read/write access to Ubiquiti databases at Amazon Web Services (AWS), which was the alleged “third party” involved in the breach. Ubiquiti’s breach disclosure, he wrote, was “downplayed and purposefully written to imply that a 3rd party cloud vendor was at risk and that Ubiquiti was merely a casualty of that, instead of the target of the attack.”
In its Jan. 11 public notice, Ubiquiti said it became aware of “unauthorized access to certain of our information technology systems hosted by a third party cloud provider,” although it declined to name the third party.
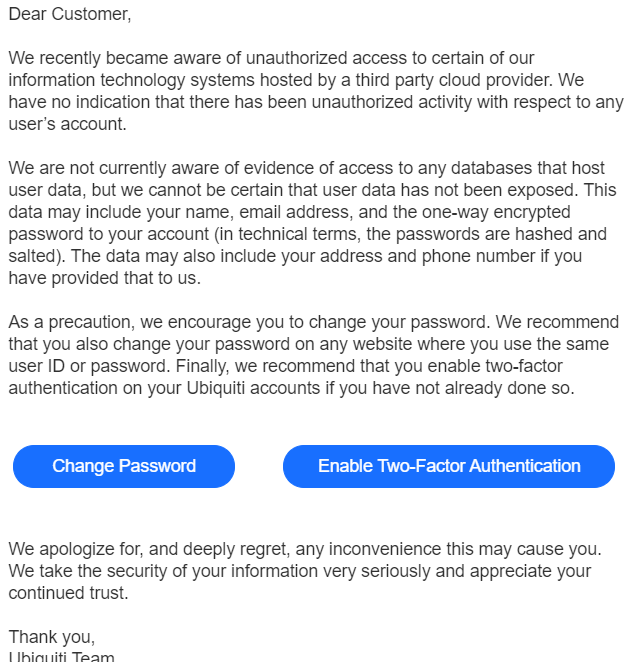
In reality, Adam said, the attackers had gained administrative access to Ubiquiti’s servers at Amazon’s cloud service, which secures the underlying server hardware and software but requires the cloud tenant (client) to secure access to any data stored there.
“They were able to get cryptographic secrets for single sign-on cookies and remote access, full source code control contents, and signing keys exfiltration,” Adam said.
Adam says the attacker(s) had access to privileged credentials that were previously stored in the LastPass account of a Ubiquiti IT employee, and gained root administrator access to all Ubiquiti AWS accounts, including all S3 data buckets, all application logs, all databases, all user database credentials, and secrets required to forge single sign-on (SSO) cookies.
Such access could have allowed the intruders to remotely authenticate to countless Ubiquiti cloud-based devices around the world. According to its website, Ubiquiti has shipped more than 85 million devices that play a key role in networking infrastructure in over 200 countries and territories worldwide.
Adam says Ubiquiti’s security team picked up signals in late December 2020 that someone with administrative access had set up several Linux virtual machines that weren’t accounted for.
Then they found a backdoor that an intruder had left behind in the system.
When security engineers removed the backdoor account in the first week of January, the intruders responded by sending a message saying they wanted 50 bitcoin (~$2.8 million USD) in exchange for a promise to remain quiet about the breach. The attackers also provided proof they’d stolen Ubiquiti’s source code, and pledged to disclose the location of another backdoor if their ransom demand was met.
Ubiquiti did not engage with the hackers, Adam said, and ultimately the incident response team found the second backdoor the extortionists had left in the system. The company would spend the next few days furiously rotating credentials for all employees, before Ubiquiti started alerting customers about the need to reset their passwords.
But he maintains that instead of asking customers to change their passwords when they next log on — as the company did on Jan. 11 — Ubiquiti should have immediately invalidated all of its customer’s credentials and forced a reset on all accounts, mainly because the intruders already had credentials needed to remotely access customer IoT systems.
“Ubiquiti had negligent logging (no access logging on databases) so it was unable to prove or disprove what they accessed, but the attacker targeted the credentials to the databases, and created Linux instances with networking connectivity to said databases,” Adam wrote in his letter. “Legal overrode the repeated requests to force rotation of all customer credentials, and to revert any device access permission changes within the relevant period.”
If you have Ubiquiti devices installed and haven’t yet changed the passwords on the devices since Jan. 11 this year, now would be a good time to care of that.
It might also be a good idea to just delete any profiles you had on these devices, make sure they’re up to date on the latest firmware, and then re-create those profiles with new [and preferably unique] credentials. And seriously consider disabling any remote access on the devices.
Ubiquiti’s stock price has grown remarkably since the company’s breach disclosure Jan. 16. After a brief dip following the news, Ubiquiti’s shares have surged from $243 on Jan. 13 to $370 as of today. By market close Tuesday, UI had slipped to $349.