Blue cheese shows off new colors, but the taste largely remains the same
Ars Technica » Scientific Method 2024-03-13
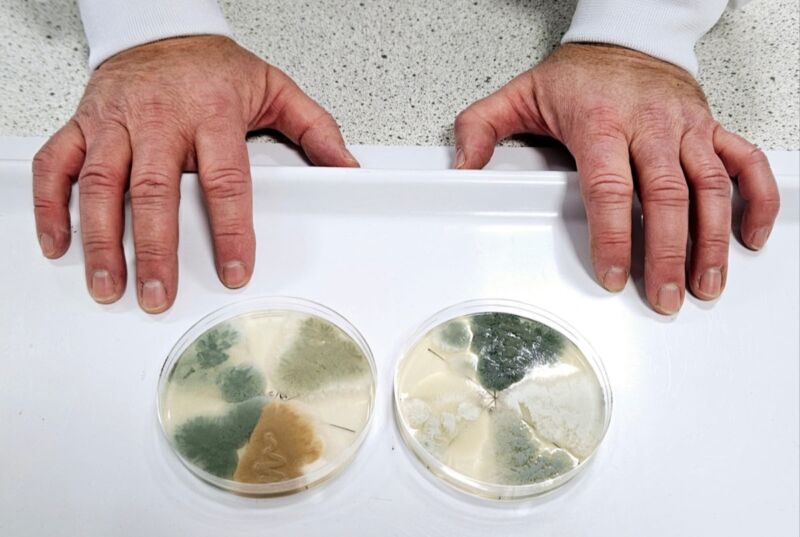
Enlarge / Scientists at the University of Nottingham have discovered how to create different colors of blue cheese. (credit: University of Nottingham)
Gourmands are well aware of the many varieties of blue cheese, known by the blue-green veins that ripple through the cheese. Different kinds of blue cheese have distinctive flavor profiles: they can be mild or strong, sweet or salty, for example. Soon we might be able to buy blue cheeses that belie the name and sport veins of different colors: perhaps yellow-green, reddish-brown-pink, or lighter/darker shades of blue, according to a recent paper published in the journal Science of Food.
“We’ve been interested in cheese fungi for over 10 years, and traditionally when you develop mould-ripened cheeses, you get blue cheeses such as Stilton, Roquefort, and Gorgonzola, which use fixed strains of fungi that are blue-green in color," said co-author Paul Dyer of the University of Nottingham of this latest research. "We wanted to see if we could develop new strains with new flavors and appearances."
Blue cheese has been around for a very long time. Legend has it that a young boy left his bread and ewe's milk cheese in a nearby cave to pursue a lovely young lady he'd spotted in the distance. Months later, he came back to the cave and found it had molded into Roquefort. It's a fanciful tale, but scholars think the basic idea is sound: people used to store cheeses in caves because their temperature and moisture levels were especially hospitable to harmless molds. That was bolstered by a 2021 analysis of paleofeces that found evidence that Iron Age salt miners in Hallstatt (Austria) between 800 and 400 BCE were already eating blue cheese and quaffing beer.